Blockchain technology is more than just a digital ledger; it’s a catalyst for change. Its significance extends far beyond cryptocurrencies, impacting finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and even how you shop online. In this article, we’ll embark on a journey to uncover the intricacies of blockchain, exploring its origins, core features, real-world applications, challenges, and potential to transform our lives.
What is blockchain?
The term blockchain consists of two words: block and chain. The simplest definition of a blockchain is that it is a chain of blocks. In other words, it consists of different blocks connected to each other like a chain. But this definition is too simple and it doesn’t answer your questions about blockchains. You may still wonder what a block is, what information it contains, and how it is connected to the previous and the next block. All these questions are normal and also useful since asking questions is the gate to understanding.
First of all, keep in mind that in the world of blockchains, everything is digital. Therefore, we have no physical blocks or chains. They are just concepts that help you understand the underlying technology better. Blocks are in fact digital spaces that contain data. These spaces are connected to each other in a specific manner.
Encryption and Cryptography in Blockchains
Encryption and cryptography play a key role in this world. We previously mentioned that each block contains some data. In blockchains, all blocks and their corresponding data are encrypted using a “hash function”. A hash function is a function that receives some human-readable input and changes it to a unique string of code consisting of numbers and letters. The hash function is a one-way function, meaning that you can’t get the input from the output. Therefore, each block has a unique unpredictable hash. All blocks in a blockchain contain the hash of the previous block. This is blockchains’ solution for connecting the blocks to each other, and this is why they are called blockchains.
Blockchains are famous for their high security. This encryption is one reason for this security. Imagine a malicious user decides to change the data of a specific block. If he succeeds to do so, the hash of that block will also change due to the change that has occurred to the input. This will further lead to a change in the data of the next block, and this will continue to the last block of the blockchain.
The Importance of Consensus in Blockchain Networks
Another important feature blockchains rely upon is “consensus”. In a blockchain network, no single entity can make decisions alone. Instead, decisions are made only if 51% of the network’s participants agree with them. Just compare it with a centralized company in which the manager makes all decisions and the employees are forced to obey.
However, how this consensus is reached in blockchain networks is a technical process and needs to be clarified. Stay with us in the next section to learn everything about consensus in blockchains.
What is a consensus in blockchains and how is it reached?
Do you remember that we said in the world of blockchains, everything is digital? Well, this is also true about consensus. Don’t imagine a blockchain network as a group of people sitting around and stating their opinions on an issue. The truth is that “blockchains are coded in a way that they achieve consensus through their specific consensus algorithms”. Any blockchain has its own consensus algorithm that determines its foundational features like its security and speed. Proof of work and proof of stake are the world’s two most famous consensus algorithms. We will go through each of them independently in the next part.
The proof-of-work consensus algorithm
Proof of work is the consensus algorithm of the world’s first and most popular blockchain, Bitcoin. As its name suggests, proof of work proves that some amount of work has been done. But how and why? Should this work be done by humans? No. It is actually done by special devices called “miners”. Any cryptocurrency that is based on proof of work relies on miner devices to be created, or “mined”.
Miners are given a set of complex math problems to solve. They are coded in a way that they solve these problems as quickly and correctly as possible, but they spend a great deal of electricity on this. By the way, the problems they solve have no other practical functions and they are just a solution to prove that some work has been done. This ensures the security of proof-of-work networks since if a malicious user wants to attack the network, he/she must pay the cost, spend the same amount of electricity, and do the same amount of work. This is both practically and economically impossible.
Miners through their calculations check the validity of the requested transactions. For example, imagine someone wants to spend a coin she has spent before. Miners will validate the request, figure out the malicious activity, and decline it. Even if some miners agree with this transaction, they cannot record it on the blockchain since 51% of the miners must agree with it.
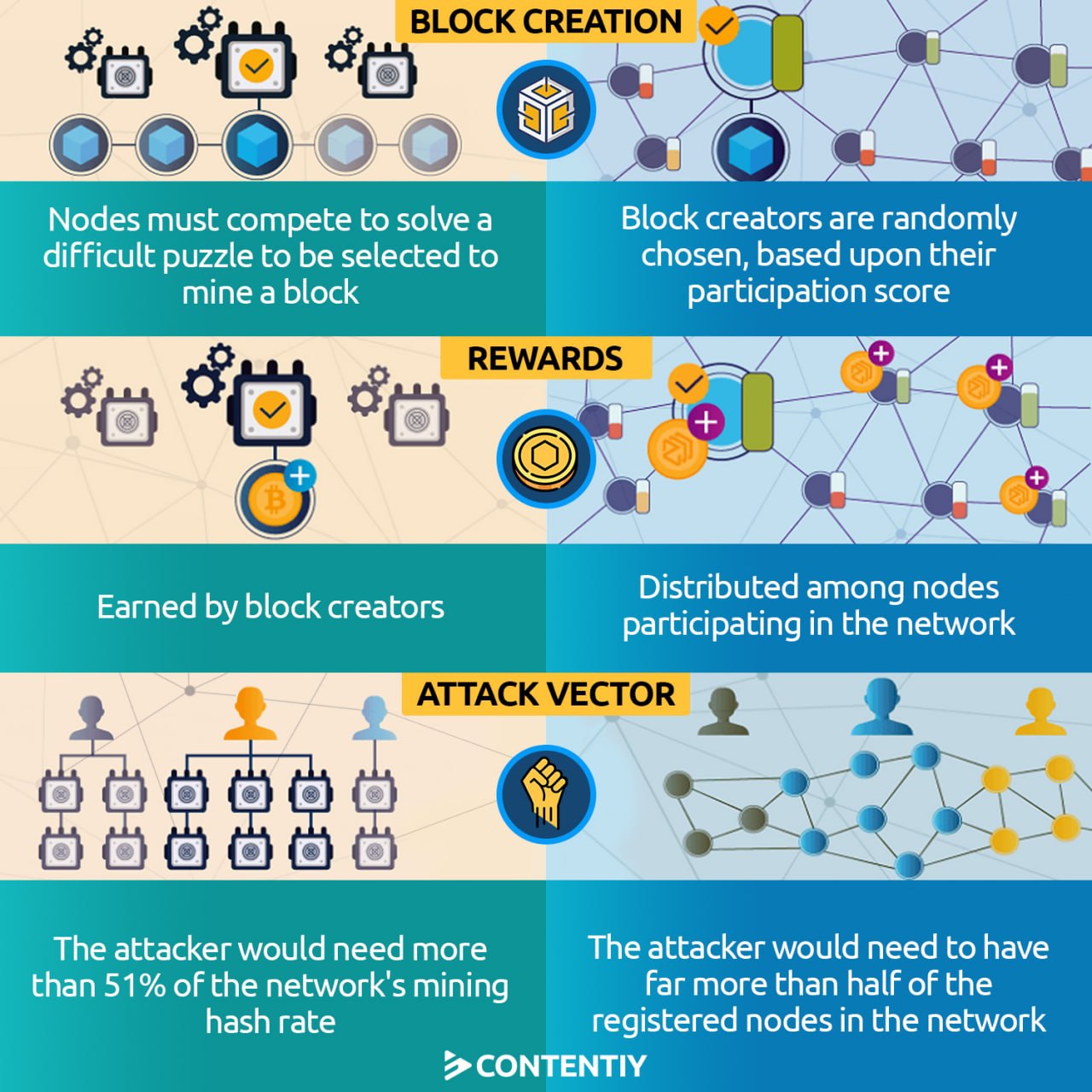
As you see, miners play a crucial role in the security of Bitcoin and other proof-of-work cryptocurrencies. In return, they get rewarded for each block they make. The reward is actually the newly minted coins distributed among miners. This way, miners have a good incentive for securing the network, and newly minted coins also get distributed in a decentralized manner.
The proof-of-stake consensus algorithm
In spite of its high security, proof of work suffered from two problems: being slow and being costly. Proof of work consumes a significant amount of electricity and it is not eco-friendly at all. In response to these problems, proof of stake emerged. Proof of stake doesn’t require miner devices. The validators (or full nodes) in proof-of-stake networks are users who stake a certain amount of that blockchain’s native cryptocurrency. The idea behind proof of stake is that validators are holders of the network’s coin, so they won’t do activities that harm the network’s security and decrease its coin’s value.
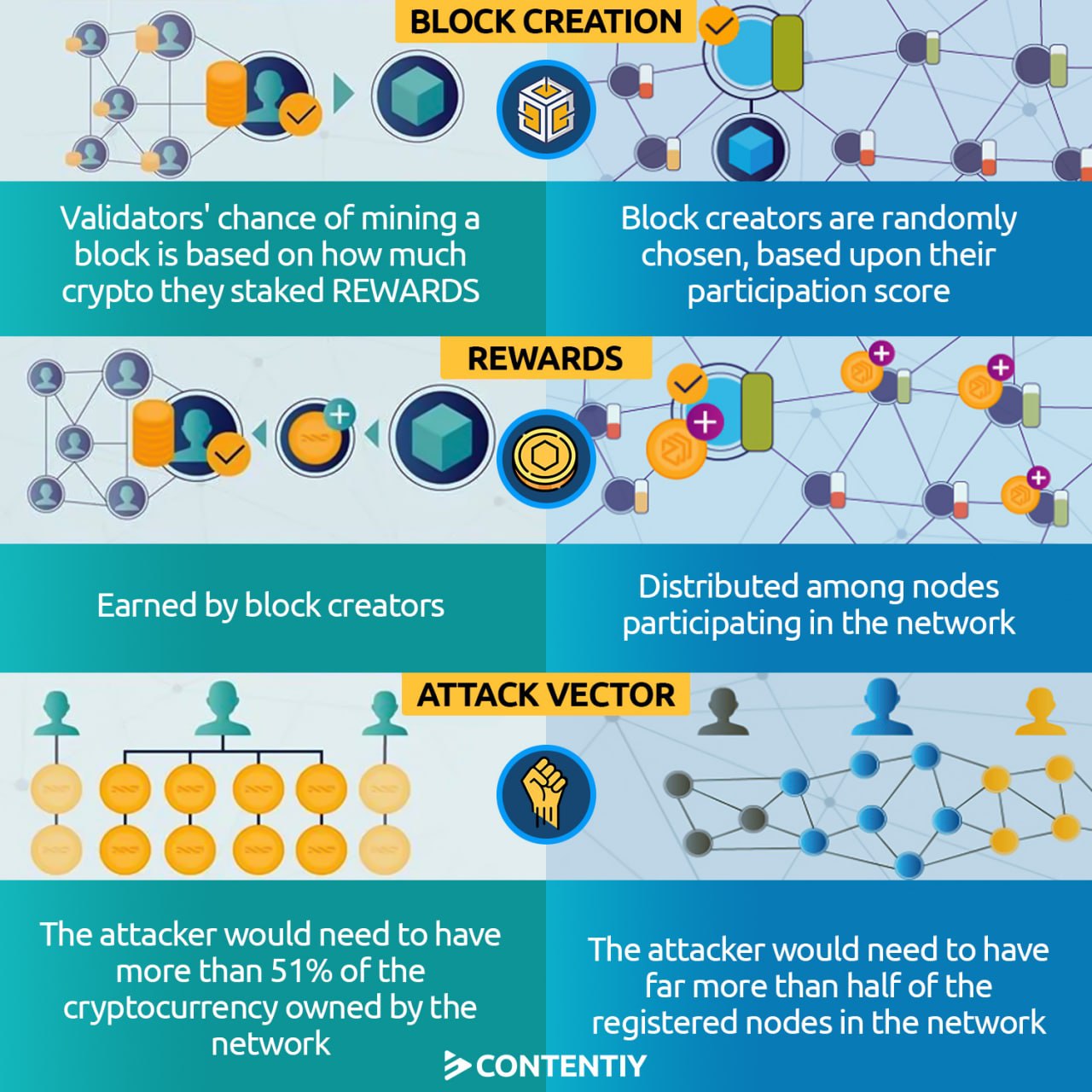
Proof of stake is faster and more eco-friendly, and it has become so popular in recent years. Nearly all new cryptocurrencies are using different forms of proof of stake. Ethereum which is the world’s second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap is still using proof of work, but it is going to migrate to a proof-of-stake network in the near future.
Is blockchain a synonym for cryptocurrency?
Many people mistakenly believe that blockchains are only useful for cryptocurrencies, but this is not the case. Although blockchain technology existed before cryptocurrencies, Bitcoin was the first project to utilize it. Blockchains have a diverse range of use cases, such as in financial systems, electronic voting, insurance, healthcare, data storage, identification, intellectual property, supply chains, real estate, and public transportation. Blockchains provide a trustless solution for governance and data storage in all areas that require it.
Conclusion
Blockchain is a relatively new technology that records data in an unchangeable permanent manner. It is actually a database, but its difference from traditional databases is that it is not based on a single or a few centralized servers, but it is distributed among all computers connected to the network. Due to their highly secure encryption systems and consensus algorithms, blockchains are not easily hacked. Bitcoin was the first real-world use case of this technology, but it can be used in all systems that wish to remove third parties.