What is a node in blockchain?
A node is a device connected to the blockchain that oversees and ensures the validity of the transactions. Each node has a unique ID belonging to this device. This ID differentiates the node from other nodes.
The best way to understand the concept of a node is to compare it with traditional financial systems. In traditional financial systems, banks were responsible for validating and making transactions. They checked the requests they received, and if no problems existed, they made the transactions.
This method had several problems. The biggest problem was its centralization, and the other issues also stemmed from this centralization. Banks had complete control over users’ accounts, transactions, and access to their identity information. They could ban transactions from/to specific parts of the world. Users had to reach the legal age to be able to have an account. These are only a few limitations traditional banks impose on their users.
Cryptocurrencies have come to solve these problems. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum consist of millions of computers from all over the world. These computers are called nodes and are responsible for validating the transactions.
Each node in blockchain is similar to a point or an intersection. All nodes are put together to form a network. As soon as a user decides to make a transaction, their request is broadcasted throughout the network. This request includes details like the amount to be transferred, the sender’s address, the recipient’s address, and so on.
One important thing that nodes check is whether the sender has enough cryptocurrencies for this transaction. If everything is OK, the transaction gets enough confirmations and is done. This is the reason blockchain transactions usually take a few minutes.
The difference between a light node and a full node
Nodes are usually divided into full nodes and light nodes. This division is based on the amount of data a node contains.
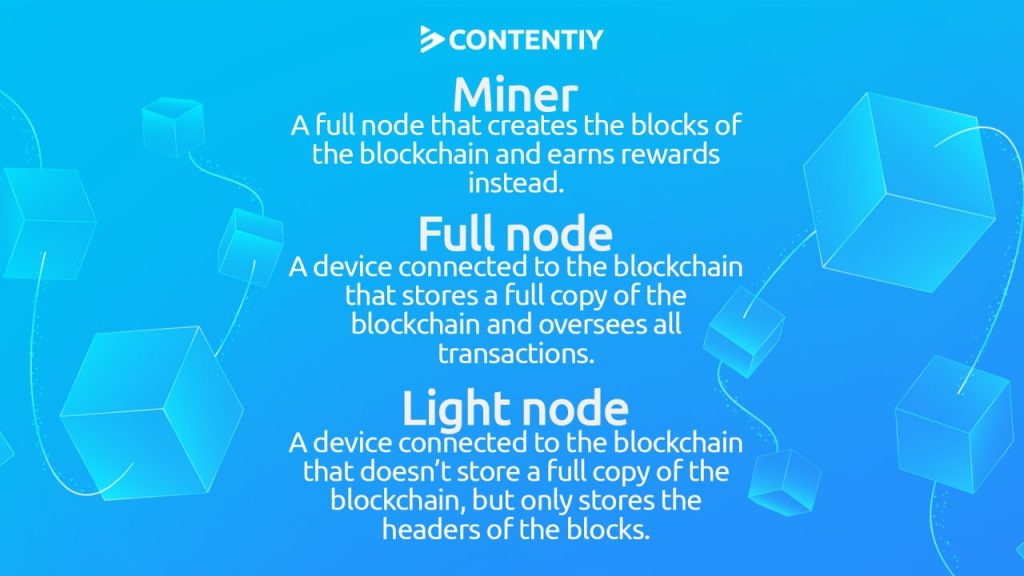
A light node doesn’t store the complete version of the blockchain. It only stores the headers of the blocks. The header is the part containing the most important information about a block. So, as it is obvious, light nodes only store the necessary data and disregard unnecessary details. For this reason, light nodes are also called Simplified Payment Verification or SPV nodes.
Full nodes are servers of decentralized networks. They validate the transactions and participate in the consensus. On the other hand, full nodes store all data related to the transactions on their devices.
The difference between a full node and a miner
You may be familiar with what miners are. Miners are special computers used for mining Bitcoin and other proof-of-work cryptocurrencies. They are ASIC devices that validate the transactions of proof-of-work cryptocurrencies and create their blocks. Creating blocks and earning rewards is what differentiates miners. All miners are full nodes, but not all full nodes are miners. Miners can add new blocks to the blockchains, but not all full nodes can. Miners can earn rewards and have income, but not all other full nodes can.
Conclusion
In this article, we tried to explain the concept of a node in the simplest terms. Now you know we have light nodes, full nodes, and miners. We have to mention that nodes have other categories. Master nodes and staking nodes are two more examples. However, light and full nodes are more common, and you may encounter them in the blockchain context.
What is a node in blockchain technology?
A node in blockchain technology refers to any device that is connected to a blockchain network and helps to maintain the network by validating transactions and storing a copy of the blockchain ledger.
What are the different types of nodes in a blockchain network?
There are different types of nodes in a blockchain network, including full nodes, light nodes, and supernodes. Full nodes have a complete copy of the blockchain ledger, light nodes only keep a subset of the blockchain data, and super nodes have additional responsibilities such as network management.
What is the function of a node in blockchain network?
The function of a node in a blockchain network is to validate transactions, maintain a copy of the blockchain ledger, and broadcast new transactions and blocks to other nodes in the network.
How is a node different from a miner in a blockchain network?
A miner in a blockchain network is a type of node that performs the additional function of adding new blocks to the blockchain by solving complex mathematical problems. Not all nodes are miners, but all miners are nodes.
Can anyone become a node in blockchain network?
In theory, anyone can become a node in blockchain network by downloading the appropriate software and connecting to the network. However, there may be technical requirements or resource constraints that limit who can effectively run a node.
How many nodes are typically in a blockchain network?
The number of nodes in a blockchain network can vary widely depending on the specific blockchain, but some blockchains have thousands or even millions of nodes.
What are the benefits of having a decentralized network of nodes in a blockchain?
The benefits of having a decentralized network of nodes in a blockchain include increased security, resistance to censorship, and greater transparency and accountability.
How can a node be added to a blockchain network?
A node can be added to a blockchain network by installing the appropriate software and connecting to the network. In some cases, there may be additional requirements such as providing proof of stake or meeting certain technical specifications.



One Response
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!